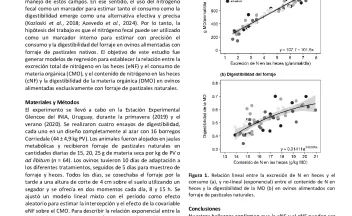
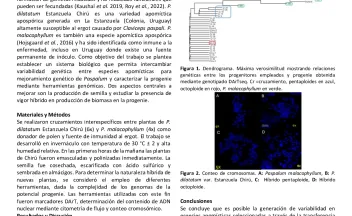
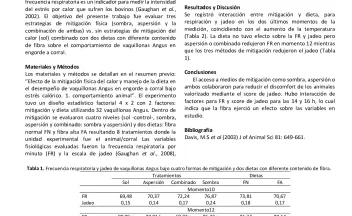
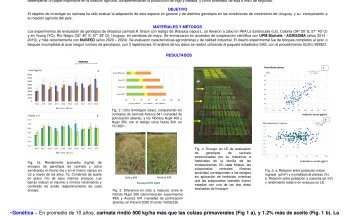
Respuesta de la cobertura de Eryngium horridum a la intensidad de pastoreo en pastizales naturales de Uruguay. (PP 8). [Response of Eryngium horridum cover to grazing intensity on natural grasslands of Uruguay.]. [abstract].
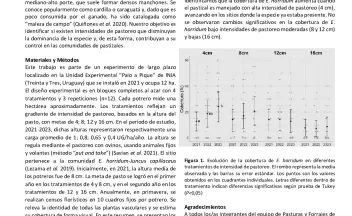
El diseño de prácticas de manejo que promuevan el incremento de la productividad ganadera y favorezcan la conservación de la biodiversidad de los pastizales del Río de la Plata debe basarse en el entendimiento de la dinámica entre las plantas y los animales. En este trabajo se presenta el efecto de la intensidad de pastoreo en una de las plantas nativas más conspicuas de dichos pastizales: Eryngium horridum Malme (Apiaceae).