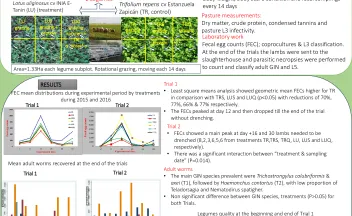
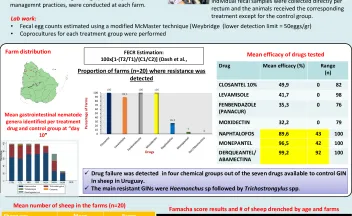
Efecto residual de herbicidas imidazolinonas sobre la implantación y desarrollo inicial de especies forrajeras sembradas en sistemas de rotación con arroz. [resumen].

En Uruguay el uso de herbicidas imidazolinonas (IMIs) es la principal herramienta utilizada para el manejo de arroz rojo en el cultivo de arroz. El objetivo de este trabajo fue cuantificar por medio de bioensayos, el potencial efecto residual de los herbicidas IMIs aplicados en el cultivo de arroz sobre la implantación y desarrollo inicial de especies forrajeras sembradas en estas rotaciones.